
| Navigating withholding tax is a common challenge for business owners, impacting their financial management. This article aims to clarify what withholding tax is, its importance, and how to manage it effectively. By understanding these concepts, you’ll be better equipped to handle your business finances confidently. |
Business people are likely to find themselves frequently engaged in “receiving money” and “paying money.” But can you believe that a significant obstacle to receiving and paying money is the withholding tax? Many business owners do not understand what it is, why it is important, and what they need to do about it. This article will explain everything you need to know.
If you want to become a top-notch business owner who receives and pays correctly, you can’t miss this article. We will guide you through everything related to withholding tax from start to finish.
เลือกอ่านได้เลย!
ToggleWhy Withhold Taxes?
Withholding tax is when the “payer” deducts a portion of the tax before paying the “payee,” and then remits the withheld tax to the Revenue Department.
The main objectives of withholding tax are as follows:
1. To pay taxes in advance:
For example, Mr. A has an annual income that requires him to pay 100,000 Baht in taxes, but the payer withholds and remits 30,000 Baht in advance. At the end of the year, Mr. A only needs to pay an additional 70,000 Baht (100,000 – 30,000).
This means that Mr. A has had his tax withheld and has been paying it in advance, so he doesn’t have to pay a lump sum at the end of the year.
2. To guarantee tax payments to the government:
From the government’s perspective, they also need to generate revenue from tax collection. With withholding taxes applied each time the money is paid, it ensures that the government gradually receives tax payments from individuals and corporations.
3. To verify whether taxpayers report their income correctly:
When the payer withholds taxes and remits them to the Revenue Department, this creates a record of the income and taxes for the payee. Therefore, if the income earner does not file their tax at the end of the year, the Revenue Department can easily detect inaccuracy and notify them to correct their annual taxes filing.
Who is Responsible for Withholding Tax?
The law mandates that the “payer” must withhold taxes whenever they make payments for expenses specified by law. Besides withholding taxes, a withholding tax certificate must be issued to the “payee” as evidence. Finally, at the end of each month, the “payer” must compile the withholding tax records to remit to the Revenue Department.
FlowAccount makes it easy for business owners to issue withholding tax certificates themselves and download reports for tax filing.

Who Gets Withheld Taxes?
Those who will be subject to withholding tax are the “payees,” which can be both individuals and legal entities. However, not all types of expenses require withholding taxes.
What types of expenses require withholding taxes? And what are the rates? We’ve summarized it in the following table.
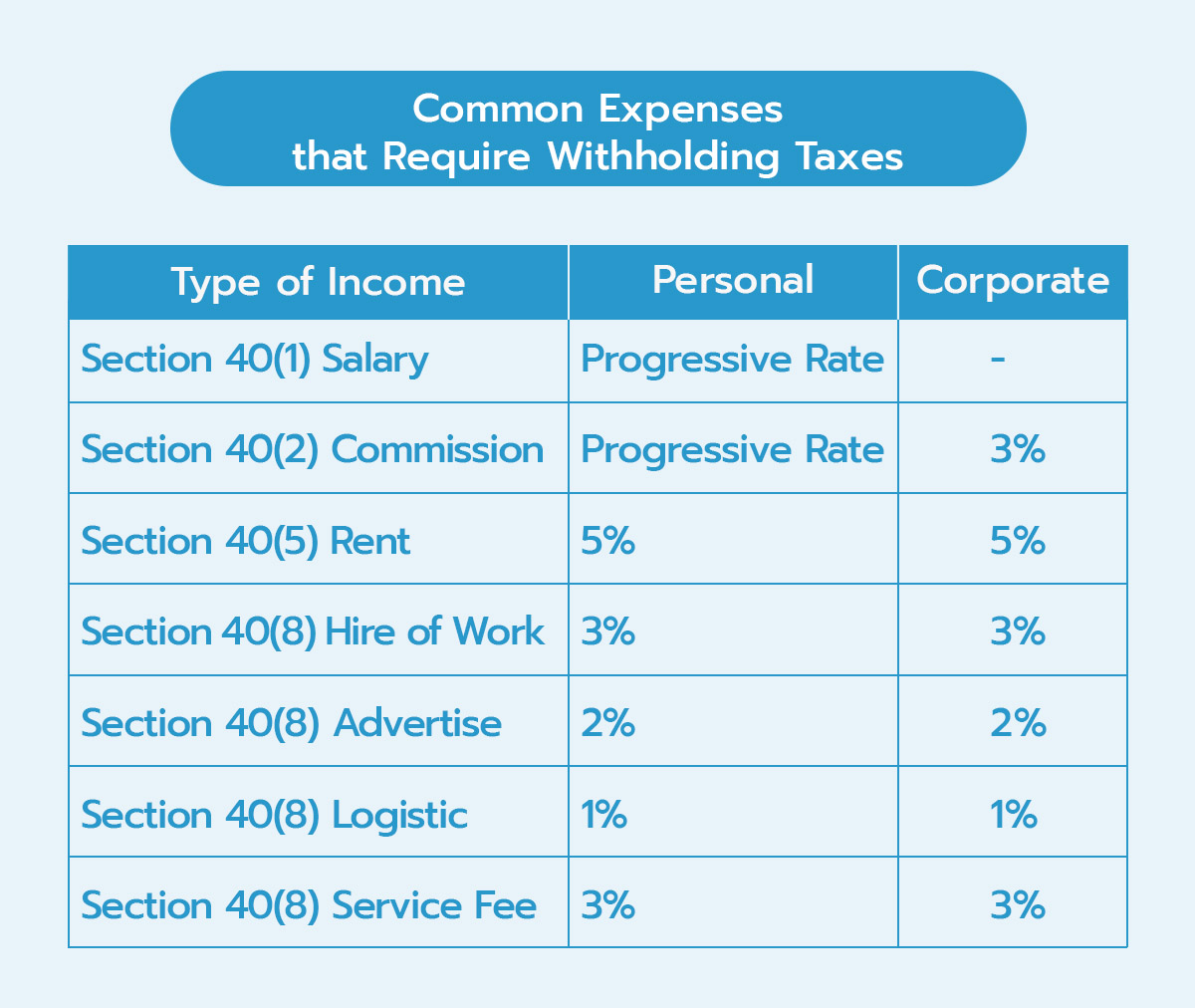
The table above lists common types of expenses we encounter in daily life. If you observe closely, the law does not mandate withholding tax for product sales. Therefore, those who buy products do not need to worry about this.
On top, withholding taxes must be applied when payments exceed 1,000 Baht, except in the case of long-term contracts where the invoice amount is less than 1,000 Baht but exceeds 1,000 Baht when accumulated for the year. The payer still needs to withhold taxes.
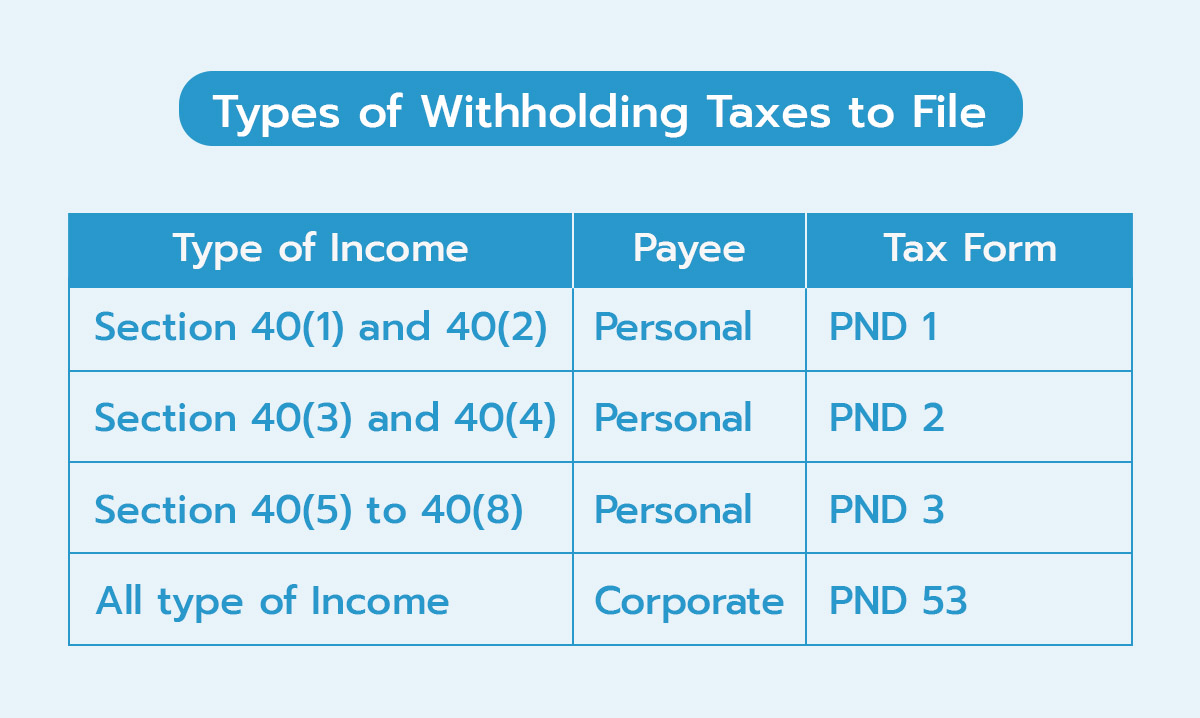
Types of Withholding Taxes to File
When taxes are withheld, a report for the withheld tax must be compiled and submitted to the Revenue Department within 7 days of the following month. The type of withholding tax filing form depends on the type of income and the type of payee.
How is Withholding Tax Calculated?
Once you understand withholding tax, if you want to become a top-notch business owner, you need to know how to calculate it. Withholding tax is not difficult to calculate if we know the type of expense and the tax rate. Here, we provide examples of two cases:
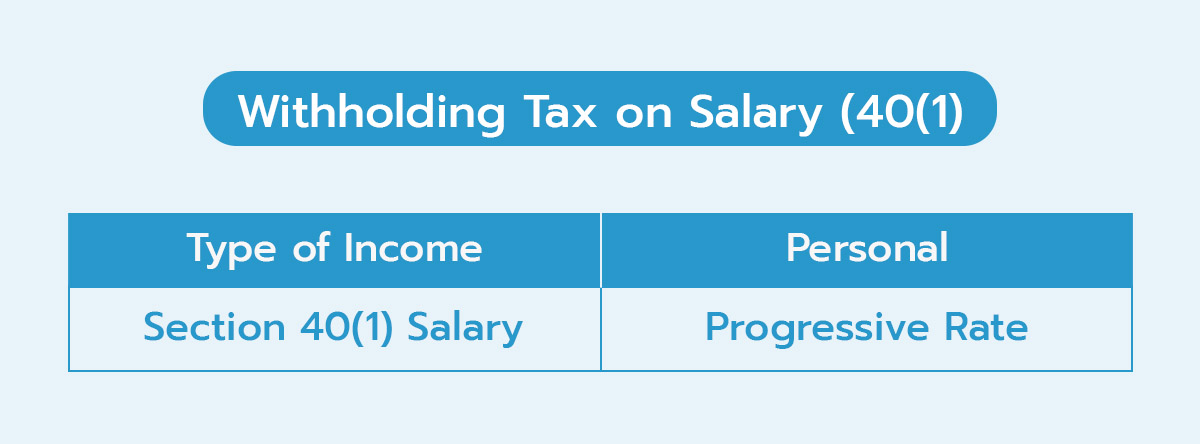
1. Withholding Tax on Salary (40(1))
Calculating withholding tax for salary payments made to individuals is based on the progressive personal income tax rate.
For example:
Monthly salary: 50,000 Baht x 12 = 600,000 Baht/year
Expenses = 100,000 Baht/year
Deductions = 60,000 Baht/year
Net income = 440,000 baht/year
Annual personal income tax:
1 – 150,000 Exempt
150,001 – 300,000: 5% = 7,500 Baht
300,001 – 500,000: 10% = 140,000 x 10% = 14,000 Baht
Total income tax for the year = 21,500 Baht
The employer must withhold 21,500/12 = 1,791.67 Baht per month and remit it to the Revenue Department using Form PND 1 every month.
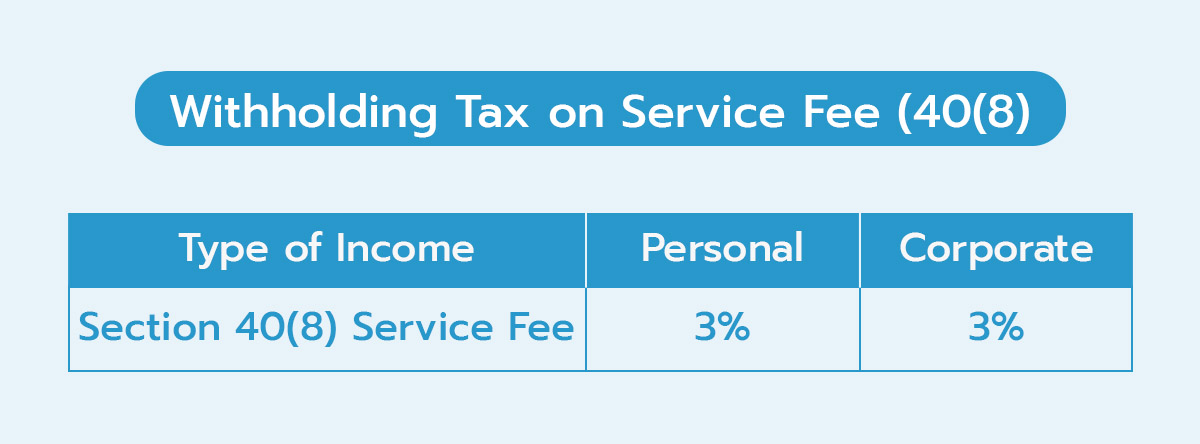
2. Withholding Tax on Service Fees (40(8))
Calculating withholding tax for service payments to individuals or legal entities has a withholding rate of 3%.
The calculation for withholding tax is based on the service fee amount excluding Value Added Tax (VAT), as follows:
Service fee: 100,000 Baht
VAT 7% = 7,000 Baht
Withholding tax 3% = 100,000 x 3% = 3,000 Baht
Net service fee to be paid = 100,000 + 7,000 – 3,000 = 104,000 Baht.
As you can see, withholding tax may seem complex at first, but it’s actually quite simple once you break it down. By taking the time to learn the basics step by step, even new business owners can easily improve their understanding and skills!
About Author

Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Thailand with experience as an external auditor for listed companies who aspires to make accounting easy and accessible for everyone.
Apply to be a writer for FlowAccount here.



